 Retinal laser photocoagulation is a non-invasive procedure used to treat leaking blood vessels in the retina that stem from serious retinal conditions such as:
Retinal laser photocoagulation is a non-invasive procedure used to treat leaking blood vessels in the retina that stem from serious retinal conditions such as:
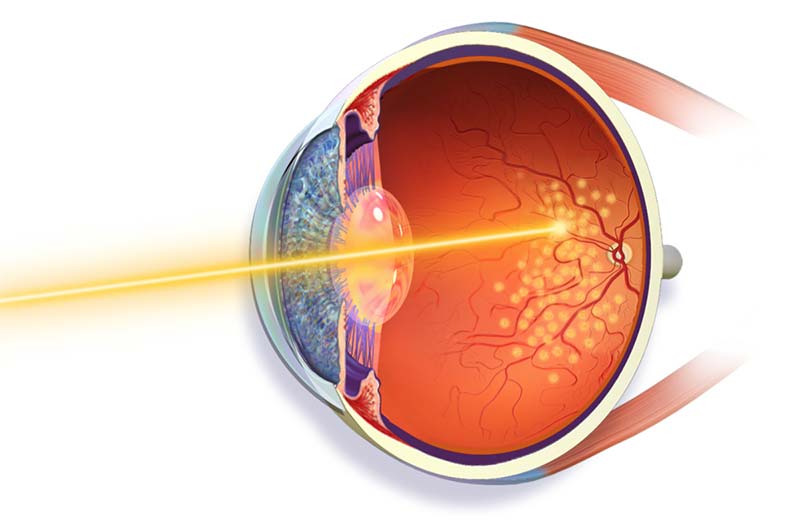
During laser photocoagulation, laser burns are made on the retina to target leaking blood vessels or slow the growth of new abnormal vessels. It’s also a form of retinal tear surgery, which aims to prevent further vision loss by creating tiny burns or scars around the retinal tear. While this procedure generally cannot restore vision that has already been lost, it can significantly reduce the risk of additional vision impairment.
Retinal laser photocoagulation is performed in the office. The retinal specialist will apply a local or topical anesthetic to the eye and dilate the pupil. In addition, a special contact lens may be placed in front of the eye to focus the laser. The specialist will then target the laser to heat up the retinal tissue and treat the retinal condition.
Adhering diligently to the post-operative guidelines provided by the retina specialist is crucial for a successful recovery. Patients may need someone to drive them home after the procedure since the pupils will be dilated for several hours. Generally, no prescription medications are necessary post-treatment, which means patients can return to their routine daily activities almost immediately.
The patient may experience blurry vision and mild pain for up to two days after the procedure. Retinal laser photocoagulation is non-invasive and has no risk of infection; however, it does carry some other potential risks, including:
The potential vision loss caused by the laser photocoagulation procedure is far less than the severe vision loss that can occur as a result of retinal conditions like diabetic retinopathy.
Download Patient Instructions for Care after Laser Treatment