- On this page: How is it Performed?
- What is Expected After?
Pneumatic retinopexy is a minimally invasive office procedure typically used to treat rhegmatogenous retinal detachments. A bubble of gas is injected into the eye and positioned over the retinal tear, allowing for fluid to pump out from beneath the retina to repair the detachment.
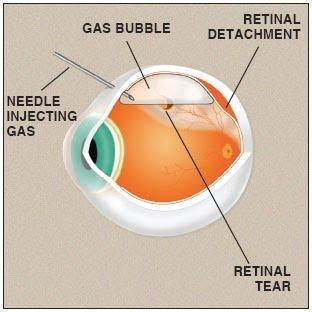
The pneumatic retinopexy procedure is performed in the office under a local anesthetic.
The retina specialist will apply eye drops to dilate the eye and make the area numb. A gas bubble will be injected into the eye shortly before or after freezing and/or laser therapy is used to seal the causative retinal tear.
The gas bubble will remain in the eye for 2 to 8 weeks on average.
It is important to follow the retina specialist’s aftercare instructions. Patients will need to arrange for someone to drive them home after the procedure. They may also need to wear an eye patch for a day or two.
After this procedure, it is critical for the patient to maintain proper head positioning for most of the day for approximately one week to allow for proper retinal re-attachment. Ideal positioning depends on the exact location of the causative retinal tear. The doctor will provide you with ideal positioning as well as other post-pneumatic retinopexy surgery recovery instructions.
Most patients experience positive results after one treatment. If the pneumatic retinopexy fails to fix the retinal detachment, patients may require vitrectomy and/or scleral buckling for definitive repair.
Although considered safe, there are minor risks associated with pneumatic retinopexy surgery, including:
Patients should call their physician if they experience any of the following after this procedure: